Spring Framework

Spring Framework에 이해하기 위해서는 먼저 프레임워크가 무엇인지, 라이브러리와의 차이가 어떤건지 알고 가는게 중요하다. 라이브러리는 내가 필요할 때 사용하는 기능이고, 프레임워크는 프레임워크에 정해진 규칙을 따라서 개발을 해야한다.
스프링 프레임워크는 여러 라이브러리는 제공하고, 그것을 활용해서 개발한 프로그램을 동작시킨다.
스프링 프레임워크(Spring Framework)는 자바 플랫폼을 위한 오픈 소스 애플리케이션 프레임워크로서 간단히 스프링(Spring)이라도 한다. 동적인 웹 사이트를 개발하기 위한 여러 가지 서비스를 제공하고 있다.
대한민국 공공기관의 웹 서비스 개발 시 사용을 권장하고 있는 전자정부 표준프레임워크의 기반 기술로서 쓰이고 있다.
출처 : 위키백과
스프링 프레임워크에서 가장 중요한 특징은 의존성 주입(Dependency Injection)이다.
의존성 주입(DI)은 클래스 사이의 의존관계를 빈(Bean) 설정 정보를 바탕으로 컨테이너가 자동으로 연결해주는 것이다.
DI가 적용되지 않으면 개발자가 직업 인스턴스를 생성해야한다.
HelloService service = new HelloService();DI를 적용하면 annotiation인 @Component, @Autowired를 이용해서 선언 해주면 된다.
@Component
public class HelloService {
}
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private HelloService service;
}
Spring Boot

Spring Boot와 Spring Framework가 전혀 다른 새로운 기술이라고 오해하는 사람들이 있는데 Spring Boot는 Spring Framework를 조금더 편하게 사용할 수 있게 해주는 툴이다.
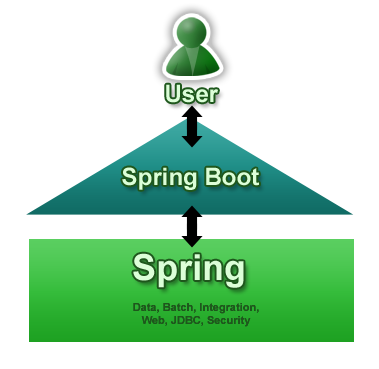
Spring Boot와 Spring Framework는 차이가 있다.
-
Spring Boot 내부에 Tomcat이 포함되어 있기 때문에 설치를 하거나 매번 버전을 관리해 주어야 할 필요가 없다.
-
Spring Framework에서는 dependency를 일일이 맞추어야 했지만 Spring Boot에서는 starter를 통한 dependency관리를 자동으로 해준다.
간단히 정리하자면 Spring Boot는 간편한 설정, 편리한 의전성 관리 & 자동 버전 관리, 내장 서버로 인한 간단한 배포 서버 구축, 다른 스프링 프레임워크 요소를 쉽게 사용하는 것이라고 생각한다.
'Web > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] DAO 와 DTO (0) | 2020.12.25 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] Spring MVC 구조 (0) | 2020.12.25 |
| [Spring] DI (Dependency Injection, 의존성 주입) (0) | 2020.12.17 |
| [Spring] MyBatis 란? (0) | 2020.12.15 |
| [Spring] Maven 과 Gradle (0) | 2020.12.13 |